Dendrogram simple template create guides axis edit step
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re a data scientist or someone interested in data analytics, you’ve probably heard of dendrograms. They’re visual representations of hierarchical clustering that show the relationships between data points. But the process of drawing a dendrogram can be confusing and intimidating, especially if you’re a beginner. In this article, we’ll dive deep into how to draw a dendrogram and break it down into easy-to-follow steps.
The Pain Points of Drawing a Dendrogram
When it comes to drawing a dendrogram, many people get stuck at the beginning. They don’t know where to start or what data to input. Additionally, figuring out how to interpret the results of the dendrogram can be challenging if you don’t have a good understanding of hierarchical clustering. Lastly, there are many software options to choose from, and picking the right one can seem like a daunting task.
How to Draw a Dendrogram
First, you’ll need to select the data you want to visualize. This can be done in a variety of ways, such as through clustering algorithms like k-means or hierarchical clustering. Once you have your data, you’ll need to input it into a dendrogram software. There are many free and paid options, including R, Python, and MATLAB. Once your software is up and running, you can input your data and customize how the dendrogram looks. Finally, you’ll need to interpret the results and draw insights from the data.
Main Points to Keep in Mind
When drawing a dendrogram, it’s important to remember to choose the appropriate hierarchical clustering algorithm, determine the distance metric, and select the optimal number of clusters. Additionally, understanding the orientation, node coloring, and branch styling can help better communicate your findings to others.
Why Dendrograms Are Important
Dendrograms are important because they can help identify patterns and relationships in data that were previously unknown. They can also help with data segmentation and decision-making. Personally, I’ve found dendrograms to be useful in my research when examining co-authorship relationships and identifying potential research collaborations.
Dendrogram Software Options
R is a popular and free option for creating dendrograms. Python is also commonly used and has packages such as Matplotlib and Scipy. MATLAB is a paid option but can provide more advanced customization options. Ultimately, the software you choose will depend on your experience level, data type, and visualization needs.
Interpreting Dendrogram Results
Interpreting dendrogram results can be challenging, but there are several key things to look for. First, you’ll want to identify any major clusters or groups within the data. Next, you’ll want to look at the height of each node, which can represent the degree of similarity or dissimilarity between data points. Finally, you’ll want to consider any patterns or relationships that emerge from the dendrogram.
The Benefits of Dendrograms
Dendrograms offer several benefits, including the ability to identify relationships and patterns in large sets of data quickly. They can help with decision-making and segmentation, and they can be customized to fit individual needs. Additionally, dendrograms can be used in a variety of fields, such as biology, sociology, and marketing.
Choosing the Right Dendrogram Software
When choosing a dendrogram software, it’s important to consider your data type, experience level, and visualization needs. Free options such as R and Python can be great if you are just starting or have a limited budget. MATLAB is a paid option but offers more advanced customization and analysis options.
Q&A about How to Draw a Dendrogram
Q: What is a dendrogram, and why is it important?
A: A dendrogram is a visual representation of hierarchical clustering that shows the relationships between data points. It is important because it can help identify patterns and relationships in data that were previously unknown.
Q: What software options are available for drawing dendrograms?
A: There are many software options available, including R, Python, and MATLAB. The software you choose will depend on your experience level, data type, and visualization needs.
Q: How do I interpret the results of a dendrogram?
A: To interpret the results of a dendrogram, look for major clusters or groups within the data, consider the height of each node, and identify any patterns or relationships that emerge.
Q: What are some common pain points when drawing a dendrogram?
A: Common pain points include choosing the appropriate hierarchical clustering algorithm, determining the distance metric, and selecting the optimal number of clusters. Understanding the orientation, node coloring, and branch styling can also be challenging.
Conclusion of How to Draw a Dendrogram
Learning how to draw a dendrogram can seem intimidating at first, but once you understand the process, it can be a powerful tool for analyzing and visualizing data. With the right software and a good understanding of hierarchical clustering, anyone can create meaningful and informative dendrograms.
Gallery
Examples Of Dendrograms Visualization - Datanovia
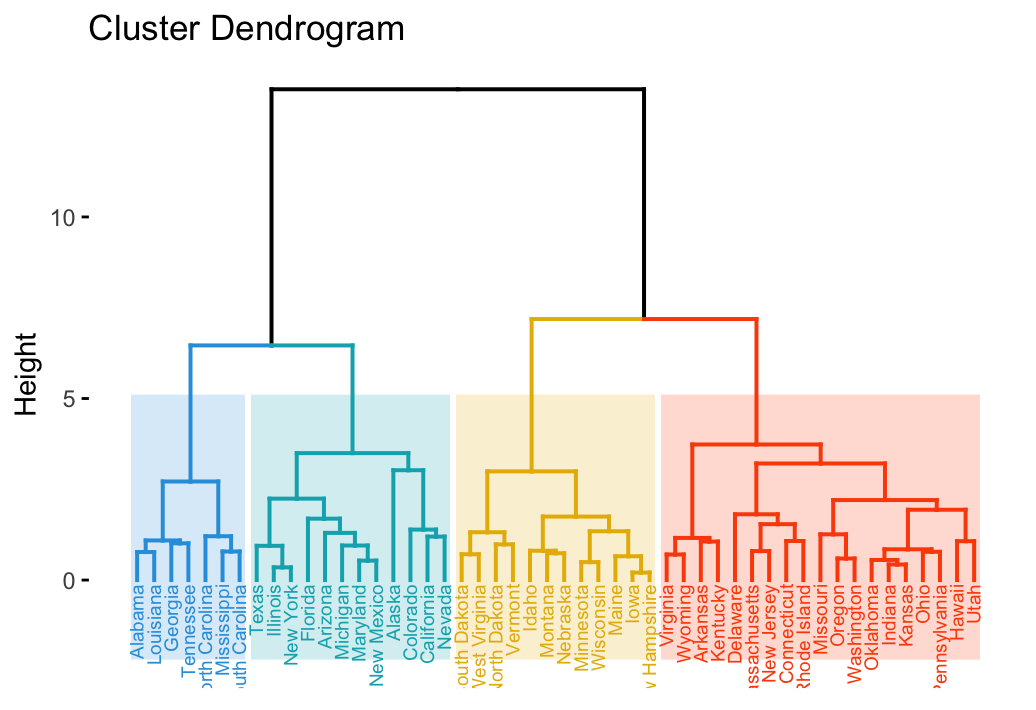
Photo Credit by: bing.com / clustering dendrogram hierarchical dendrograms d3 ggplot2 color cluster fviz dend plot visualization unsupervised learning edges straight clusters datanovia theme labels
Wie Zeichnet Man Ein Dendrogramm - Wissenschaft 2023

Photo Credit by: bing.com /
Simple Guides To Create Dendrogram
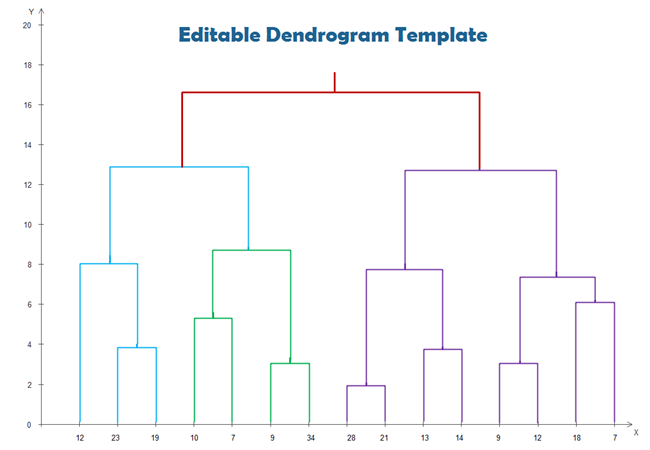
Photo Credit by: bing.com / dendrogram simple template create guides axis edit step
Circular Dendrogram - Categorical Classification - Phyo Phyo Kyaw Zin
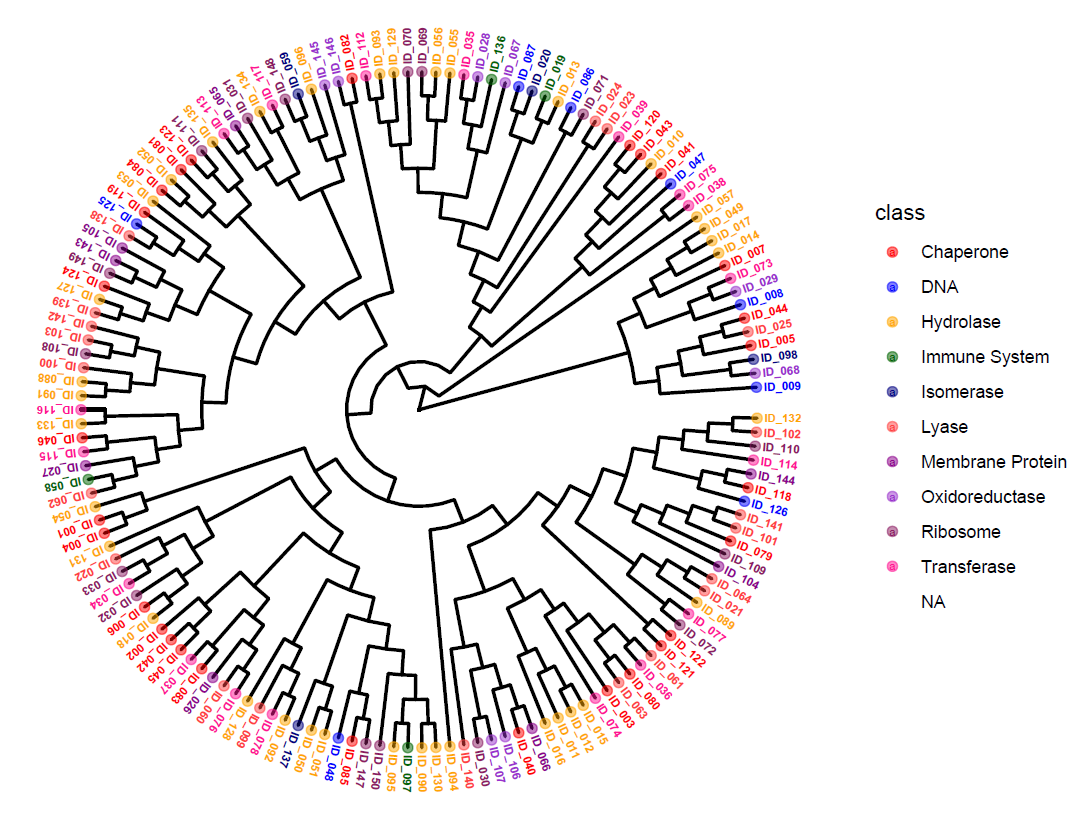
Photo Credit by: bing.com / dendrogram categorical classification zin phyo kyaw cheminformatics
Python 3.x - How To Draw Dendrogram In Matplotlib Without Using Scipy

Photo Credit by: bing.com / dendrogram matplotlib using scipy draw without attempt replicate trying below